订阅邮件推送
获取我们最新的更新
Quarterly Report on China’s Deleveraging (Q1 2018)
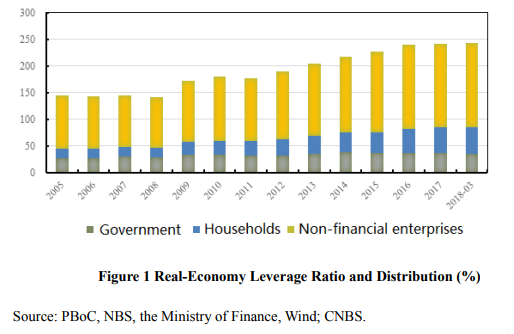
I. Overall Leverage Ratio Slightly Increased with Significant Progress in Structural Deleveraging Although the Chinese government announced the deleveraging goal in October 2015, China’s overall leverage ratio did not abate until 2017, when the leverage ratio only increased by 2.3 percentage points. This growth rate has reduced substantially compared with the annual average growth rate of 12.3 percentage points since the eruption of the global financial crisis. Q1 2018 marked a good beginning for China’s deleveraging process. Despite a slight increase in overall leverage ratio, structural deleveraging made significant progress. First, overall real-economy leverage ratio slightly increased. In Q1 2018, the real-economy leverage ratio encompassing the household sector, non-financial enterprises and the government sector increased to 243.7%, up 1.6 percentage points from 242.1% at the end of 2017. The uptrend was relatively stable. The leverage ratios of the household sector and non-financial enterprises both increased: Compared with the end of 2017, household sector leverage ratio increased by 1.0 percentage point, and the leverage ratio of non-financial enterprises rose by 1.2 percentage points. The leverage ratio variations of various sectors are shown in Figure 1.
作者相关研究
Author Related Research
- 暂无 Null
相关研究中心成果
Relate ResearchCenter Results
- 暂无 Null

